Geography Pages
Prehistoric Sites
All boundaries, and borders of countries, are approximate
The territory controlled by a king or people varied from time to time, and was often disputed by other peoples. Even the coast-line has varied over the years, particularly in the Gulf of Persia. An approximation to the modern coast-line is generally used in the maps. The sites of some ancient cities and towns are now not known with certainty
Prehistoric refers to the time before writing came into use, and generally includes the Stone and early Chalcolithic Ages.
There were prehistoric communities in Egypt also, but the annual flooding of the Nile has destroyed most traces of them
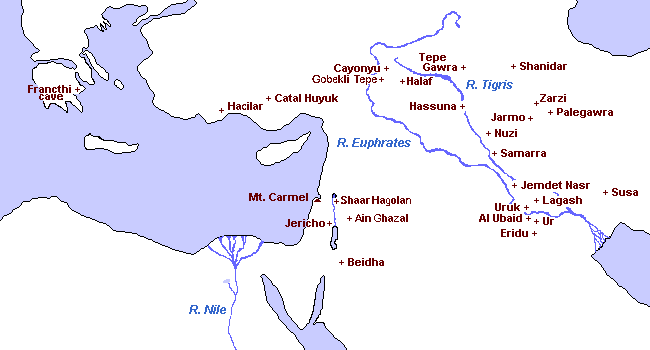
Notes : Not all the places and peoples shown existed simultaneously
Palaeolithic (Old Stone Age - cave dwellers, hunting and fishing) remains have been found in caves at Kebara in Mount Carmel (the Kebaran culture), at Shanidar, Zarzi, and Palegawra in Mesopotamia, and the Francthi cave in Greece.
Neolithic (New Stone Age - with the introduction of farming and houses and eventually pottery) cultures have been identified at the Wadi al Natuf (the Natufian culture) by Mount Carmel, and at Jericho, Beidha, Catal Huyuk, Cayonyu, Hassuna, and Jarmo.
Chalcolithic (intermediate between Stone and Bronze Ages, the first experiments in metal-working, and the earliest beginnings of writing) sites have been found at Al Ubaid (the Ubaid culture), Ur, Uruk (now called Warka), Tell Halaf, Tepe Gawra, Jemdet Nasr, Samarra, and Susa.
![]() Go here for the Time-line of Ancient History.
Go here for the Time-line of Ancient History.
Copyright © 1999 Shirley J. Rollinson, all Rights Reserved